In 1943, an American Psychologist, Abraham Maslow, proposed that the physiological need of humans governs their decision-making skills. 1n 1954, Maslow published a book, Motivation, and personality, to define five basic steps of the Hierarchy of needs. Maslow’s Hierarchy theory is related to the organizational theory of motivation because it presents ways to increase human motivation. The formers define what people need, and the latter defines how needs differ among people. For example, for some people, the purpose of work is money, while others love to work to be respected by others. Told by experts of cheap essay writing services, this theory suggests ways to increase employees ‘motivation level by considering five needs;
In terms of physiology, Self-actualization is a process through which a man can reach his full potential. Kurt Goldstein, a physiatrist, first described this term in the 20th century. According to a physiatrist, all human actions are goal-oriented. And these goals target the decision-making abilities of a human. Maslow follows the same theme of Self-actualization and hence places it at top of the pyramids.
This example will help you understand the self-actualization needs of different people. For example, some people want to be ideal parents while others want to be good leaders. Still, others want appreciation for their art of creativity.
This theory explains that esteem needs are among the most prominent needs that encourage them to achieve their goals in children and infants.
Based on love and belongingness needs, people often decide whether to join certain groups of people or not. The presence of people you love will motivate you to work in a team. Examples of love based needs are trust, friendship, companionship, and expectations from others.
In contrast, lack of needs responds to four levels of self-reality; physical needs, security, love, and self-confidence. The need for scarcity arises from a person’s desire to eliminate defects or obtain items that are not available. When people get things, they do not have, their motivation to get them decreases.
This model explains that if these needs are not fulfilled in the employees, they get frustrated. Therefore, the lack of job satisfaction and motivation results from lacking all the needs mentioned above. For example, if a worker is very energetic at the start of this career and remains unappreciated in terms of money or respect, he will lose motivation. Therefore, Maslow’s Hierarchy theory helps the administration motivate their employees by considering their potential needs.
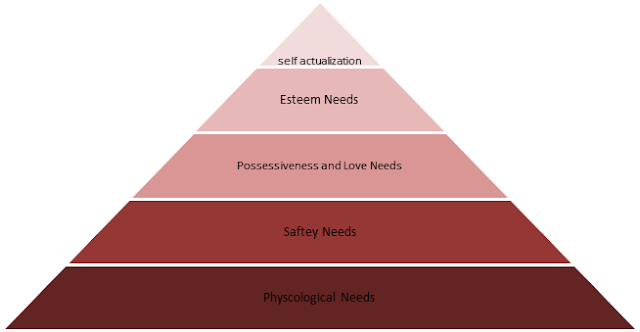
- Self-actualization
- Esteem Needs
- Possessiveness and love Needs
- Safety Needs
- Physiological Needs

Pyramid of Maslow Hierarchy of Needs
Self-Actualization Needs:
Self-actualization needs stand at the top of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs pyramid, as shown in Figure 1. However, self-actualization is a broader term and refers to a person’s growth requirements. At this level, the persons’ experience, self–fulfilment, and personal growth opportunities are considered to motivate employees.In terms of physiology, Self-actualization is a process through which a man can reach his full potential. Kurt Goldstein, a physiatrist, first described this term in the 20th century. According to a physiatrist, all human actions are goal-oriented. And these goals target the decision-making abilities of a human. Maslow follows the same theme of Self-actualization and hence places it at top of the pyramids.
This example will help you understand the self-actualization needs of different people. For example, some people want to be ideal parents while others want to be good leaders. Still, others want appreciation for their art of creativity.
Esteem Needs:
‘Esteem Needs’ include self-belief, strength, self-respect, confidence, and elements like respecting others. Maslow’s theory of Hierarchy explains that the factors of esteem help to develop self-actualization. However, esteem is multifactorial and governed by many external factors. Therefore, in Maslow Hierarchy pyramid, esteem needs are placed at the second layer of the pyramid. Maslow, in his model, categorizes esteem needs into the following parts;- In some people, esteem needs include desires to attain master, dignity, achievements, or independence.
- While another type of esteem people sets targets to attain professional grace, appreciation, and reputation.
This theory explains that esteem needs are among the most prominent needs that encourage them to achieve their goals in children and infants.
Love and Belongingness Needs:
Love and belongingness needs are at the third layer of the pyramid of Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs. According to many philosophers, love is a physiological and emotional bond between people and their belongings. Love is the extreme form of affiliation, attraction, and commitment between individuals. However, the most common needs of people are desires to attain dream cars, dream houses, and otherworldly objects. The love of materialistic objects is belongingness while affiliation with people is love.Based on love and belongingness needs, people often decide whether to join certain groups of people or not. The presence of people you love will motivate you to work in a team. Examples of love based needs are trust, friendship, companionship, and expectations from others.
Safety Needs:
The strong desire of the people to be safe and secure is called “security requirements”. Therefore, the Fourth level of the Maslow Hierarchy of needs pyramid is related to safety. When a person’s emotional needs are met, a sense of security and safety can be sacrificed. People want to know how to judge, examine, and control their lives. Community and relatives can meet these needs. Generally, schools, hospitals, societies, and the army are responsible for fulfilling public security needs. Examples of safety needs include housing security, climate security, freedom from fear, health and well-being, as well as economic security.Physiological Needs:
The next step of Maslow’s Hierarchy of needs guide is the conceptual understanding of psychological needs. According to the definition, Psychological needs are the human biological requirements necessary for survival. These requirements include shelter, air, water, cold in summer and warmth in winter, rest, employment, and the most important of all, motivation. The availability of these basic needs satisfies a man.Maslow’s Growth vs. Needs:
Maslow divides his Hierarchy into two different types of needs; deficiency needs and growth needs. The difference between deficiency and growth needs is the alteration in motivation levels after attaining the needs. Greater motivation is needed to achieve growth. In contrast, motivation decreases by attaining deficiency needs. As mentioned earlier, self-realization is about achieving personal growth, which is essential. The need to grow arises from the desire to grow as a better person. When a person meets a growing need, his motivation increases as his desire to be better grows.In contrast, lack of needs responds to four levels of self-reality; physical needs, security, love, and self-confidence. The need for scarcity arises from a person’s desire to eliminate defects or obtain items that are not available. When people get things, they do not have, their motivation to get them decreases.
Significance of Maslow Hierarchy of Needs:
The article by experts of cheap essay writing services provides the list of the needs presented by Maslow. These needs are arranged in a hierarchical form. Hierarchy is started from the most basic need to the highest need. The order of the need in a hierarchy is not rigid; it depends on human preferences and differences. The needs are found to be flexible and evolved with time. Some humans have multi-needs depending upon their necessities. Human motivation is primarily dependent on these hierarchies of needs. When these needs are fulfilled, the motivation of an employee is also increased. Hence, the motivated employee performs the job with the highest efficiency.This model explains that if these needs are not fulfilled in the employees, they get frustrated. Therefore, the lack of job satisfaction and motivation results from lacking all the needs mentioned above. For example, if a worker is very energetic at the start of this career and remains unappreciated in terms of money or respect, he will lose motivation. Therefore, Maslow’s Hierarchy theory helps the administration motivate their employees by considering their potential needs.
